In the pharmaceutical industry, data integrity is a fundamental regulatory requirement and a critical element in ensuring consistent product quality and patient safety. Accordingly, and in this context, the ALCOA principles serve as the core framework for establishing reliable and compliant data practices.
We recognize the vital role that accurate, consistent, and reliable data plays in upholding our commitment to compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and delivering high-quality pharmaceutical products.
History of ALCOA:
The ALCOA story began in the last century when Stan Wollen, an FDA Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) inspector, started training fellow inspectors on new inspection techniques. As a result, he developed the acronym to help them not only understand but also effectively evaluate GLP study data for quality rather than just integrity. Interestingly, since the ALCOA company’s aluminum kitchen foil was widely available at the time, he cleverly leveraged its name to define five key criteria that could be applied to any data set.
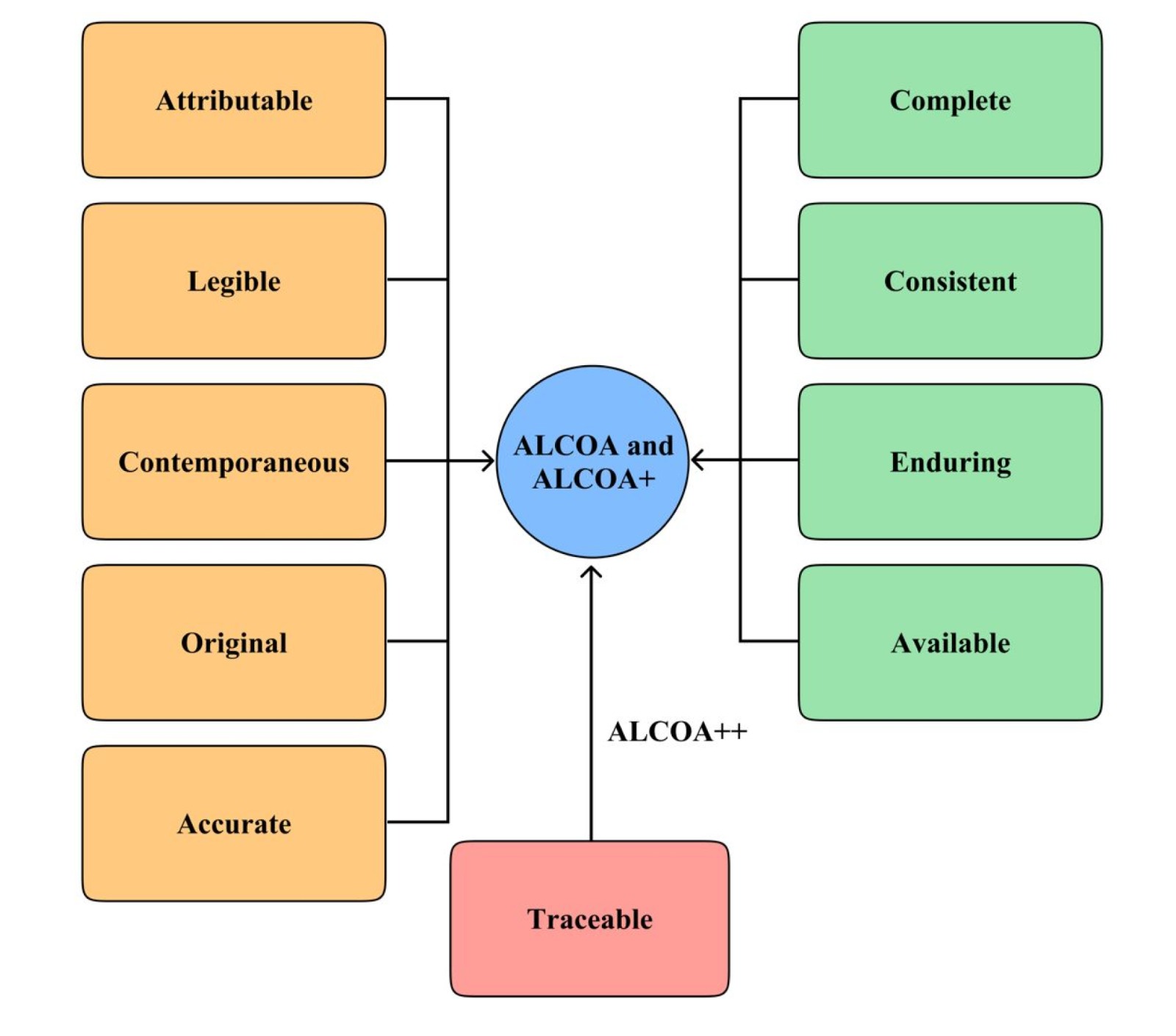
- Attributable
- Legible
- Contemporaneous
- Original
- Accurate.
Wollen outlined these criteria in a publication titled Data Quality and the Origin of ALCOA, which is available for download online (1). He emphasized that existing Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and GLP regulations already included these elements.
However, he organized them into a simple, memorable acronym (2).
What is ALCOA?
| Table 1: Meaning of ALCOA | |
| Criterion | Meaning |
| Attributable | Ensure Clear Identification: Capture information in records to uniquely identify the originator, whether a person or a computer system ((3). Assign Responsibility: Hold individuals accountable for performing, reviewing, and authorizing activities. ((4) Track Actions and Timing: Specify who acquired the data or performed subsequent actions and when they occurred. Link Measurements: Connect each measurement to a uniquely identified instrument, equipment, or item that provided the value. Prevent Orphan Data: Associate data with a project, study, batch, or lot to maintain traceability. |
| Legible | Ensure Readability: Maintain data in a clear and understandable format, whether electronic or paper-based. Support Traceability: Present a clear sequence of steps or events to allow full reconstruction of GXP activities.(3) Maintain Permanence: Preserve records throughout the retention period specified by applicable GXP guidelines.(4) Verify Metadata and Entries: Ensure all electronic metadata and written entries remain legible. Review Audit Trails: Confirm that all recorded entries, including those in the audit trail, are readable and comprehensible. |
| Contemporaneous | Record Data Immediately: Document data at the time they are generated or observed.(3) Ensure Timely Documentation: Capture information on paper or electronically during the activity. Identify Time Sources Clearly: Specify the time source for accuracy in records. Use a Trusted Time Source: Ensure computerized systems rely on a secure and reliable time reference. |
| Original | Preserve Original Records: Maintain data in the file or format in which they were originally generated to ensure integrity, including accuracy, completeness, content, and meaning. Verify True Copies: Create and retain exact verified copies that preserve the content and meaning of the original record.(4) Capture and Retain Original Data: Record the first or source data and all subsequent information necessary to fully reconstruct GXP activities. Review Original Data: Conduct a thorough review of original records to ensure compliance and accuracy.(3) Ensure Data Retention: Store original data and verified copies in a complete, enduring, and easily retrievable format throughout the retention period. Maintain Written and Electronic Records: Keep written observations, printouts, or certified copies, along with electronic records that include metadata.(5) Preserve Essential Metadata: Retain all essential metadata and the original record format when copying electronic data. |
| Accurate | Ensure Data Accuracy: Maintain correctness, truthfulness, completeness, validity, and reliability.(3) Prevent Errors: Avoid mistakes in original observations or recorded data. Document All Edits: Record modifications through documented amendments or audit trail entries by authorized personnel. Use Reliable Data Sources: Utilize accurate, calibrated, and controlled data sources. Track Electronic Data Changes: Document all modifications in electronic data using audit trail entries. Employ Calibrated Instruments: Ensure the use of calibrated or qualified analytical instruments. Validate Computerized Systems: Implement validated systems for data processing and storage. Apply Correct Equations: Use appropriate formulas to ensure data accuracy.(6) Perform Proper Rounding: Follow correct rounding practices to maintain precision. |
What is ALCOA+?
Add Four Criteria to make ALCOA+
In 2010, the European Medicines Agency issued guidance on electronic source data in clinical trials (7) and expanded ALCOA by adding four more criteria, creating ALCOA+. These additional criteria included:
- Complete
- Consistent
- Enduring
- Available.
Table 2 presents the definitions along with explanations. The 2021 Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention/Pharmaceutical Inspection Cooperation Scheme (PIC/S) data integrity guidance also applies the ALCOA+ criteria (8).

| Table 2: The four additional criteria of ALCOA+ | |
| Criterion | Meaning |
| Complete | Include All Data: Record all analytical data, including data generated before identifying a problem and data produced after repeating or reanalyzing the sample. Link Paper Output to Electronic Records: Ensure that paper outputs in hybrid systems directly connect to the electronic records used to generate them. |
| Consistent | Date and Time Stamp All Elements: Mark all analysis elements, including the sequence of events and data files, with date stamps for all processes. Ensure Proper Order: Apply time stamps in the correct sequence when using hybrid or electronic systems. |
| Enduring | Use Authorized Media: Ensure data is recorded in laboratory notebooks, numbered worksheets, or electronic media with proper accountability. Avoid Unapproved Surfaces: Prevent data recording on envelopes, laboratory coat sleeves, cigarette packets, sticky notes, or body parts. Store Electronic Data Securely: Maintain electronic data on controlled and robust storage media. |
| Available | Ensure Record Accessibility: Allow retrieval of all records, regardless of media, for review, audit, or inspection throughout their lifetime. Validate Data Migration: Perform validated migration for electronic and hybrid media over the retention period to maintain readability. Justify Any Data Loss: Explain and justify any data loss resulting from migration. Maintain Data Integrity: Preserve the original content and meaning of migrated data to ensure consistent decision-making. Synchronize Hybrid Records: Align migrated electronic records with their corresponding paper records. Guarantee Access After Contract Ends: Ensure data remains accessible for review, audit, or inspection even after outsourced contracts conclude. |
What is ALCOA++?
The tenth and latest ALCOA criterion is “traceable,” from a draft EMA guidance on computerized systems and electronic data in clinical trials (9). Table 3 presents the definition and meaning.
| Table 3: Traceable criterion for ALCOA++ | |
| Criterion | Meaning |
| Traceable | Ensure Data Traceability: Track data throughout its entire life cycle.(9) Maintain Change Records: Record any modifications to data, context, or metadata without obscuring the original information, and provide explanations when necessary. Document Changes in Metadata: Log all changes in metadata, such as an audit trail. Use Trusted Time Stamps: Apply time stamps traceable to a reliable time source. Track Activities Accurately: Ensure contemporaneous and consistent activities are linked to trusted timestamps. Follow Metrological Standards: Use equipment and standards traceable to international benchmarks. Obtain Reliable Calibration Standards: Source analytical reference and calibration standards from trusted suppliers. Link Work to Training Records: Establish traceability from an activity and the responsible individual to their training documentation. |
The references in Tables 1 and 2 to Table 3 suggest an inherent traceability, aligning with the ALCOA+ criteria, which emphasize the need for data to be Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate.
By pointing to Table 3, all data entries are ensured to be traced back to their source by the system, supporting key ALCOA+ principles (10).
ALCOA criteria vs Regulatory Guidance Documents
All ALCOA criteria to the respective GMP regulatory guidance documents for data integrity available at the start of 2022.
As shown, the PIC/S (8) and two EMA GCP guidance documents (7,9) include the guidelines with ALCOA+ and ALCOA++ criteria. However, reiterating my advice earlier, Appendix 1 of the WHO guidance (3) is still the must-read section to have an in-depth understanding of ALCOA, supplemented with PIC/S PI-041 (8) and the latest EMA (9) guidances for ALCOA+ and ALCOA++ criteria, respectively.
Find Table 4 for mapping of ALCOA against guidelines.
| Table 4: ALCOA mapped to Regulatory Data Integrity Guidance Documents | |||||||
| Criteria | EMA (15) | EMA (12) | PIC/5 (13) | WHO (9) | FDA (8) | WHO (7) | MHRA (6) |
| Attributable | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Legible | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Contemporaneous | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Original | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Accurate | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Complete | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Consistent | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Enduring | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Available | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Traceable | ✔ | ||||||
We understand that non-compliance with data integrity regulations can lead to severe penalties, product recalls, and damage to our reputation. Therefore, we have implemented robust systems and processes to ensure data integrity at every stage of our operations.
Summary
Traceability directly connects with ALCOA and ALCOA+ principles such as Attributable, Contemporaneous, Complete, Accurate, and Consistent by ensuring the ability to track and verify data throughout its lifecycle. It indirectly supports principles like Legible, Original, Enduring, and Available by promoting proper data management and upholding these standards. Traceability plays a crucial role in maintaining data integrity and compliance in pharmaceuticals.
Reference
(1) S.W. Wollen, Data Quality and the Origin of ALCOA in The Compass Summer 2010, Newsletter of the Southern Regional Chapter, Society of Quality Assurance (2010). Available from: http://www.southernsqa.org/newsletters/Summer10.DataQuality.pdf
(2) 21 CFR 58 Good Laboratory Practice for Non-Clinical Laboratory Studies (Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, 1978).
(3) World Health Organization, Technical Report Series No. 996 Annex 5 Guidance on Good Data and Records Management Practices (WHO, Geneva, Switzerland, 2016).
(4) MHRA, GMP Data Integrity Definitions and Guidance for Industry 2nd Edition (Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency: London, United Kingdom, 2015).
(5) WHO Handbook, Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) Quality Practices for Regulated Non Clinical Research and Development, Second Edition (World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2009).
(6) FDA 483 Observations Aurobindo Pharma Ltd. (FDA, Rockville, MD, 2021).
(7) European Medicines Agency, Reflection paper on expectations for electronic source data and data transcribed to electronic data collection tools in clinical trials (European Medicines Agency, London, United Kingdom, 2010).
(8) PIC/S PI-041, Good Practices for Data Management and Integrity in the Regulated GMP/GDP Environments Draft (Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention/Pharmaceutical Inspection Cooperation Scheme, Geneva, Switzerland, 2021).
(9) EMA Draft Guideline on Computerized Systems and Electronic Data in Clinical Trials (European Medicines Agency, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021).
(10) https://www.spectroscopyonline.com/view/is-traceability-the-glue-for-alcoa-alcoa-or-alcoa-
FAQs
What does ALCOA stand for in data integrity?
ALCOA is an acronym that represents key principles ensuring data integrity:
- Attributable
- Legible
- Contemporaneous
- Original
- Accurate
What is the difference between ALCOA and ALCOA+?
ALCOA+ expands on ALCOA by adding additional criteria to further enhance data reliability:
- Complete – All data must be included and not omitted.
- Consistent – Data should follow a logical order without contradictions.
- Enduring – Records must be preserved and remain intact.
- Available – Data should be accessible whenever required.
What is ALCOA++?
ALCOA++ further strengthens data integrity by adding Traceability, ensuring that all data entries can be traced back to their source.
Why is ALCOA important in regulated industries?
ALCOA principles ensure that data in pharmaceutical, healthcare, and other regulated sectors is reliable, verifiable, and compliant with regulatory guidelines like FDA, EMA, and PIC/S.
How does ALCOA support compliance with regulatory agencies?
ALCOA aligns with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) guidelines, ensuring that recorded data is trustworthy and meets industry standards.
Does ALCOA apply only to electronic data?
No, ALCOA applies to both electronic and paper-based records. However, electronic data systems often have built-in features that help enforce these principles more effectively.
What happens if ALCOA principles are not followed?
Non-compliance with ALCOA principles can lead to:
- Data integrity violations.
- Regulatory penalties and audits.
- Loss of product approvals.
- Legal and reputational risks for companies.
How does ALCOA help in audits and inspections?
By ensuring data is attributable, legible, and traceable, ALCOA makes it easier for regulatory bodies to verify compliance during inspections and audits.
What industries benefit from ALCOA principles?
While ALCOA is primarily used in pharmaceuticals and healthcare, it also benefits industries such as:
- Food and beverage production.
- Chemical manufacturing.
- Medical devices.
- Biotechnology research.
ALCOA full form?
- Attributable
- Legible
- Contemporaneous
- Original
- Accurate



