
Sampling in pharma is a critical quality control process. It ensures that every material and product meets strict regulatory standards for safety, efficacy, and quality before reaching consumers. Whether it’s raw materials, in-process materials, or finished products, sampling helps prevent contamination, deviation, or product failure.
What is Sampling in Pharmaceutical Industry?
Sampling is the process of taking a small, representative portion of a larger batch or lot for testing and analysis. The primary goal is to assess the quality of materials (raw, intermediate, or finished) without testing the entire batch. It is a mandatory step under Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and is closely regulated by bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and WHO.
A correct sampling process ensures:
- Compliance with specifications
- Consistency across batches
- Safe and effective pharmaceutical products
Types of Sampling in Pharma
Depending on the production stage and the type of material, there are several types of sampling practices:
1. Raw Material Sampling
- Sampling of incoming raw materials such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
- Ensures materials meet defined specifications before use.
2. In-Process Sampling
- Sampling during manufacturing to check if the process is within control limits.
- Helps detect deviations early in production.
3. Finished Product Sampling
- Conducted on the final product after manufacturing is complete.
- Ensures the product meets all required quality attributes (purity, potency, dissolution, etc.).
4. Stability Sampling
- Collecting samples over time under different environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity).
- Evaluates how the product degrades over time and determines shelf life.
5. Environmental Sampling
- Monitoring cleanrooms and manufacturing areas.
- Involves air, surface, personnel, and water sampling to ensure aseptic conditions.
Explore a leading manufacturer of APIs.
With over 10 years of expertise, we ensure GMP compliance and provide reliable, high-quality solutions.
Sampling Tools Used in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The tools used depend on the type of material (powder, liquid, granules) and the sampling point (container, equipment, environment):
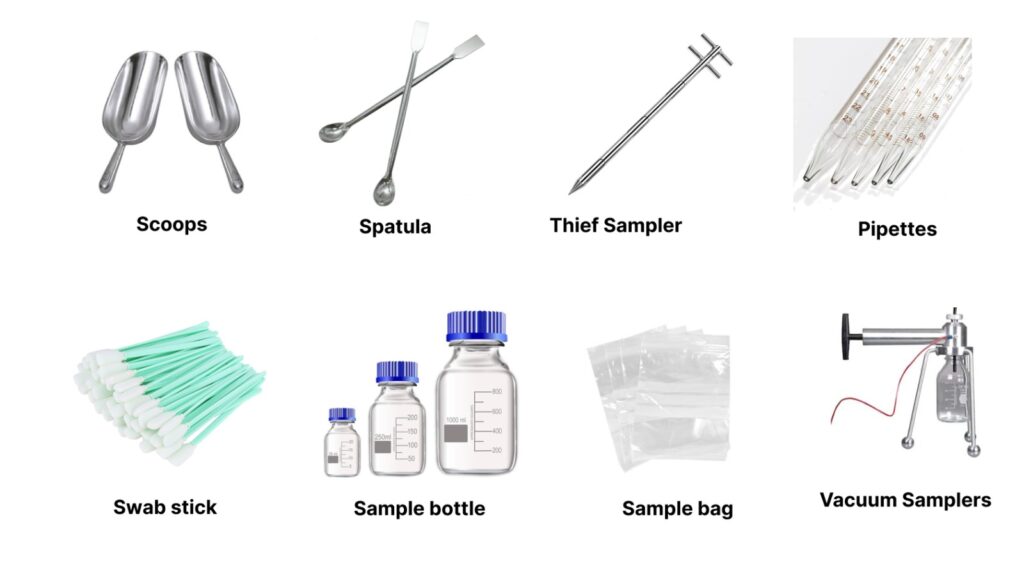
Common Sampling Tools:
- Sampling Scoops or spatula
Used for powders and granules. - Thief Sampler
A tubular device to collect samples from different depths within a drum or bag. - Liquid Sampler (Pipettes or Dippers)
Used for collecting liquid samples from tanks or containers. - Swabs
For environmental sampling (surface or equipment cleaning validation). - Vacuum Samplers
For airborne particle sampling or microbial air sampling. - Sterile Bottles & Bags
For collecting liquid or water samples. - Peristaltic Pumps
Used in environmental and liquid sampling for collecting samples aseptically.
General Sampling Procedure in Pharmaceuticals
While the exact procedure may vary depending on the type of sample, GMP guidelines require a standardized approach. Here’s a typical sampling procedure:
1. Preparation
- Review the sampling plan (based on SOPs or batch records).
- Ensure all sampling tools are clean, calibrated, and sterilized (if necessary).
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
2. Sampling Location & Identification
- Identify the correct sampling point (top, middle, bottom, or composite).
- Verify material identity (batch number, container label, etc.).
3. Aseptic Technique (if required)
- In critical environments, follow aseptic techniques to avoid contamination.
- Use sterile tools and sample containers.
4. Sample Collection
- Use appropriate tools to collect a representative sample.
- For composite samples, collect portions from different parts of the container and mix.
5. Labeling
- Label the sample with batch number, date, sample type, and sampler name.
6. Sample Transfer
- Transport the sample to the QC lab as per SOP.
- Maintain required environmental conditions (e.g., temperature-sensitive materials).
7. Documentation
- Record all sampling details in the sampling register or batch record.
- Include any deviations or observations.
Important Notes:
- Sampling should follow a risk-based approach.
- Sampling quantities should comply with pharmacopeial guidelines (e.g., USP, EP).
- Avoid cross-contamination and ensure traceability at all stages.
Conclusion
Sampling is the backbone of pharmaceutical quality control. It acts as a safeguard to ensure that only safe and effective medicines reach patients. Whether you are handling raw materials, intermediates, or finished goods, the correct tools and standardized procedures are essential for reliable results and regulatory compliance.
Chemignition Laboratory is a trusted manufacturer and exporter of pharmaceutical ingredients, operating in full compliance with GMP standards. All sampling procedures are performed as per ICH guidelines to ensure quality, safety, and regulatory adherence.
FAQs
What is sampling in the pharmaceutical industry?
Sampling in pharma refers to the process of collecting a representative portion from a batch or lot to evaluate its quality, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Why is sampling important in pharmaceuticals?
Sampling ensures that raw materials, in-process products, and finished goods meet quality and regulatory standards, preventing contamination, product failure, and ensuring patient safety.
What are the common types of sampling in pharmaceuticals?
Common types include raw material sampling, in-process sampling, finished product sampling, stability sampling, and environmental sampling.
What tools are used for pharmaceutical sampling?
Tools include thief samplers, sampling scoops, pipettes, dippers, swabs, vacuum samplers, sterile bottles, bags, and peristaltic pumps, depending on the sample type.
What is the general procedure for sampling in pharma?
The procedure involves preparation, location identification, aseptic technique (if required), sample collection, labeling, transferring the sample to QC, and documentation.
How does sampling ensure GMP compliance?
Sampling helps detect deviations, prevent cross-contamination, and ensures that every batch meets quality standards as per GMP guidelines.



