Budesonide is a corticosteroid widely used to manage inflammatory conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn’s disease. Its unique structure, chemical properties, and targeted mechanism of action make it a versatile and effective medication. This guide delves into Budesonide’s structure, properties, pharmacology, uses, and safety profile.
1. Structure of Budesonide
Understanding the molecular structure of Budesonide helps explain its efficacy in managing inflammation.
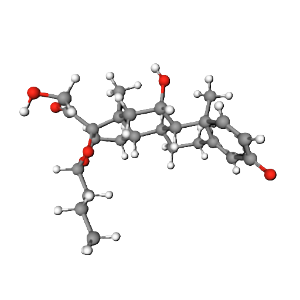
2D Structure
The 2D structure of Budesonide displays its corticosteroid backbone, characterized by its cyclic rings and hydroxyl groups. These features are essential for its anti-inflammatory properties and receptor-binding specificity.
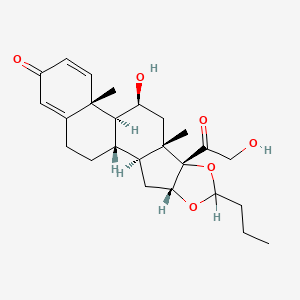
3D Structure
The 3D conformation of Budesonide reveals its spatial arrangement, highlighting its hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. These contribute to its high affinity for glucocorticoid receptors, facilitating its potent anti-inflammatory effects.
2. Names and Identifiers
Budesonide is well-documented under various names and identifiers.
- IUPAC Name:
(RS)-11β,21-dihydroxy-16α,17-[(1RS)-butylidenebis(oxy)]-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione - Molecular Formula:
C25H34O6 - Molecular Weight:
430.54 g/mol - CAS Registry Number:
51333-22-3 - Synonyms:
Pulmicort, Rhinocort, Entocort, Uceris
These identifiers facilitate its recognition across pharmacological and medical databases.
Explore a leading manufacturer of APIs.
With over 10 years of expertise, we ensure GMP compliance and provide reliable, high-quality solutions.
3. Chemical and Physical Properties
The chemical and physical properties of Budesonide contribute to its versatility and effectiveness.
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Melting Point | ~220°C |
| Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in ethanol and methanol |
| LogP (Partition Coefficient) | ~2.4 |
| pKa | ~12.0 |
| Chemical Class | Corticosteroid |
These properties allow Budesonide to be formulated for inhalation, nasal spray, and oral capsules.
4. Drug and Medication Information
Budesonide is widely used in managing respiratory and gastrointestinal inflammatory conditions.
Formulations
- Inhalation:
- Available as inhalers or nebulizer suspensions (e.g., Pulmicort).
- Nasal Spray:
- Used for allergic rhinitis (e.g., Rhinocort).
- Oral Capsules and Tablets:
- Designed for controlled release in the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., Entocort, Uceris).
Mechanism of Action
Budesonide works by:
- Inhibiting Pro-Inflammatory Mediators: Suppresses cytokines, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes.
- Activating Glucocorticoid Receptors: Reduces inflammation and immune responses.
- Minimizing Systemic Absorption: Its first-pass metabolism ensures limited systemic side effects.
Dosage and Administration
- For Asthma and COPD: Inhale twice daily using an inhaler or nebulizer as prescribed.
- For Allergic Rhinitis: One spray per nostril daily or as directed.
- For Crohn’s Disease: 9 mg orally once daily in the morning for up to 8 weeks.
Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for optimal results.
5. Pharmacology and Biochemistry
Budesonide’s pharmacology highlights its effectiveness as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption:
Rapid absorption in the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. - Bioavailability:
~10-20% due to extensive first-pass metabolism. - Half-Life:
~2-3 hours for inhaled or oral formulations. - Metabolism:
Metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P450 enzymes, primarily CYP3A4. - Excretion:
Eliminated via urine and feces.
Pharmacodynamics
Budesonide binds to glucocorticoid receptors, modulating gene expression and suppressing inflammatory pathways. This action reduces symptoms in conditions like asthma, COPD, and IBD.
6. Uses and Side Effects
Primary Uses
- Respiratory Conditions:
Effective in managing asthma and COPD by reducing airway inflammation. - Allergic Rhinitis:
Provides relief from nasal congestion and sneezing. - Inflammatory Bowel Diseases:
Treats Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis with controlled-release formulations.
Benefits
- Rapid onset of action in reducing inflammation.
- Minimal systemic effects due to localized action.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Throat irritation or hoarseness (inhaled formulations).
- Nasal dryness or irritation (nasal spray).
- Nausea or bloating (oral formulations).
Rare but serious side effects:
- Adrenal suppression.
- Increased risk of infections.
- Osteoporosis with long-term use.
Always consult a doctor if side effects persist or worsen.
7. Safety and Hazards
Safety Profile
Budesonide is generally safe when used as prescribed. However, caution is advised in:
- Pregnant Individuals: Use only if the benefits outweigh potential risks.
- Patients with Infections: May worsen fungal, bacterial, or viral infections.
Chemical Safety

Handling Precautions
- Avoid contact with eyes.
- Do not abruptly discontinue use, especially after long-term therapy.
Environmental Impact
Budesonide has minimal environmental persistence, breaking down rapidly in aquatic systems.
Chemignition Laboratory is a globally trusted manufacturer and exporter of Budesonide Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API).
We specialize in APIs and provide complete documentation support including,
- GMP Certificate
- COA
- MSDS
- Stability Data
- Impurity Profile
- ISO 9001 Certificate
Customized packaging and cold chain logistics ensure safe delivery of sensitive APIs worldwide.
We proudly serve pharmaceutical companies across the USA, Europe, Asia, and more.
Partner with Chemignition Laboratory for consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and reliable global supply.
FAQs
IUPAC Name of Budesonide?
IUPAC Name of Budesonide is (RS)-11β,21-dihydroxy-16α,17-[(1RS)-butylidenebis(oxy)]-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
Molecular Formula of Budesonide?
C25H34O6
Molecular Weight of Budesonide?
430.54 g/mol
CAS number of Budesonide?
51333-22-3
What is Budesonide used for?
Budesonide is used to treat inflammatory conditions such as:
- Asthma: Controls and prevents symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Reduces inflammation in the airways.
- Allergic Rhinitis: Alleviates nasal congestion and sneezing.
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): Treats conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
How does Budesonide work?
Budesonide is a corticosteroid that reduces inflammation by suppressing the immune response. It binds to glucocorticoid receptors, inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes.
What are the common side effects of Budesonide?
Common side effects include:
- Throat irritation or hoarseness (inhaled formulations).
- Nasal dryness or irritation (nasal spray).
- Nausea, bloating, or mild abdominal pain (oral formulations).
- Dizziness or headache.
How should Budesonide be used?
- Inhalation: Use the inhaler or nebulizer as directed, typically twice daily.
- Nasal Spray: Apply one spray in each nostril once daily or as prescribed.
- Oral Tablets/Capsules: Swallow the capsule whole, usually once daily in the morning.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions for dosage and frequency.
