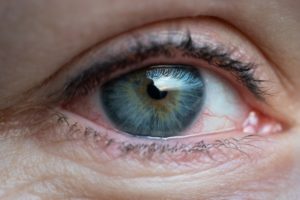
Bimatoprost is a prostaglandin analog primarily used for managing glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Its distinctive structure, chemical properties, and targeted mechanism of action make it a staple in ophthalmology. This detailed guide explores Bimatoprost structure, properties, pharmacology, uses, and safety profile.
1. Structure of Bimatoprost
Understanding the molecular structure of Bimatoprost sheds light on its unique mechanism of action.
2D Structure
The 2D structure of Bimatoprost highlights its prostaglandin analog framework, with an amide group attached to its ethyl ester side chain. This structure is key to its binding affinity and selective action on prostaglandin receptors.
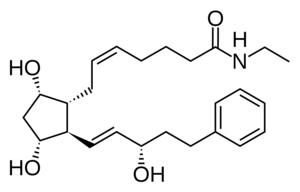
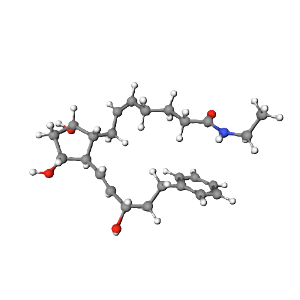
3D Structure
The 3D conformation of Bimatoprost reveals its flexible chains and planar prostaglandin core, optimizing its interaction with prostaglandin FP receptors. This interaction facilitates its ocular pressure-lowering effect.
2. Names and Identifiers
Bimatoprost is well-documented across scientific literature under various names and identifiers.
- IUPAC Name:
N-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propyl)-3-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxy-5-phenylpent-1-enyl]oxy]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl]propanamide - Molecular Formula:
C25H37NO4 - Molecular Weight:
415.57 g/mol - CAS Registry Number:
155206-00-1 - Synonyms:
Lumigan, Latisse
These identifiers make it easier to locate Bimatoprost in pharmacological databases.
3. Chemical and Physical Properties
The chemical and physical attributes of Bimatoprost are critical to its therapeutic applications.
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, colorless to slightly yellow liquid |
| Melting Point | Not applicable (liquid state) |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide |
| LogP (Partition Coefficient) | ~3.5 |
| pKa | ~4.0 |
| Chemical Class | Prostaglandin analog |
These properties make Bimatoprost an ideal candidate for ophthalmic formulations.
👉 Chemignition Laboratory provides Bimatoprost with strict adherence to ICH stability conditions and offers custom packaging for global shipping.
4. Drug and Medication Information
Bimatoprost is primarily indicated for managing elevated intraocular pressure and enhancing eyelash growth.
Explore a leading manufacturer of APIs.
With over 10 years of expertise, we ensure GMP compliance and provide reliable, high-quality solutions.
Formulations
- Ophthalmic Solution:
- 0.01% and 0.03% concentrations.
- Cosmetic Solution:
- Used for promoting eyelash growth (e.g., Latisse).
Mechanism of Action
Bimatoprost works by:
- Increasing Aqueous Humor Outflow: Enhances both uveoscleral and trabecular meshwork outflow to lower intraocular pressure.
- Stimulating Hair Growth: Extends the growth phase of eyelashes.
Dosage and Administration
- For Glaucoma/Ocular Hypertension: One drop in the affected eye(s) once daily in the evening.
- For Eyelash Growth: Apply to the upper eyelid margin with a sterile applicator once daily in the evening.
Always follow your physician’s instructions to avoid overuse or contamination.
5. Pharmacology and Biochemistry
Bimatoprost’s pharmacology highlights its prostaglandin analog properties, leading to its therapeutic effects.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption:
Rapidly absorbed through the cornea after topical application. - Bioavailability:
~12-15% systemic absorption. - Half-Life:
~45 minutes, leading to minimal systemic exposure. - Metabolism:
Primarily metabolized in the liver via oxidation, N-deethylation, and glucuronidation. - Excretion:
Eliminated via urine and feces.
Pharmacodynamics
Bimatoprost activates prostaglandin FP receptors, increasing aqueous humor outflow and lowering intraocular pressure. Its action on hair follicles enhances eyelash growth by extending the anagen phase.
6. Uses and Side Effects
Primary Uses
- Ocular Hypertension and Glaucoma:
Reduces elevated intraocular pressure to prevent optic nerve damage. - Cosmetic Applications:
Approved for enhancing eyelash length, thickness, and darkness.
Benefits
- Proven efficacy in lowering intraocular pressure.
- Enhances eyelash appearance for cosmetic use.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Ocular irritation (burning, itching).
- Conjunctival hyperemia (eye redness).
- Increased pigmentation of the iris or eyelids.
- Unwanted hair growth near application areas.
Rare side effects:
- Allergic reactions.
- Blurred vision or changes in eye pressure.
Consult a doctor if side effects persist or worsen.
7. Safety and Hazards
Safety Profile
Bimatoprost is generally safe when used as prescribed. However, it is contraindicated in:
- Patients with hypersensitivity to Bimatoprost or its components.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, unless specifically advised by a doctor.
Chemical Safety

Handling Precautions
- Avoid touching the dropper tip or applicator to prevent contamination.
- Discontinue use if significant irritation or allergic reactions occur.
Environmental Impact
Bimatoprost degrades rapidly in aquatic environments, posing minimal ecological risk.
Manufacturing Standards at Chemignition Laboratory
At Chemignition Laboratory, we manufacture high-purity, GMP-certified Bimatoprost API for pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies worldwide.
What Sets Us Apart:
- GMP-certified facility
- Custom batch sizes for formulation partners
- Stability and impurity profile data
- Ready-to-share CoA, MSDS, and DMF filing support
- Global export experience
Conclusion
Bimatoprost is a proven, safe, and effective API with growing demand across ophthalmology and aesthetic medicine. Whether you’re formulating for glaucoma, ocular hypertension, or cosmetic lash enhancement, choosing a reliable API supplier is key.
📢 Contact Chemignition Laboratory for GMP-certified Bimatoprost API today.
- Get high-purity API
- CoA, DMF, MSDS available
- Global shipping & regulatory support
👉 Contact Us for bulk quotes, samples, or technical data sheets.
FAQs
IUPAC Name of Bimatoprost?
N-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propyl)-3-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxy-5-phenylpent-1-enyl]oxy]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl]propanamide.
Molecular Formula of Bimatoprost?
C25H37NO4
Molecular Weight Bimatoprost?
415.57 g/mol
CAS No of Bimatoprost?
155206-00-1
What is Bimatoprost used for?
Bimatoprost is used for lowering intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension. It is also used cosmetically to enhance eyelash growth, making them longer, thicker, and darker.
How does Bimatoprost work?
Bimatoprost increases the outflow of aqueous humor through the uveoscleral pathway and trabecular meshwork, reducing intraocular pressure. It also prolongs the growth phase (anagen phase) of eyelashes, enhancing their length and thickness.
Can Bimatoprost change the color of my eyes?
Yes, Bimatoprost can cause increased pigmentation of the iris, which may result in permanent darkening of the eye color, especially in individuals with hazel or light-colored eyes.
Can Bimatoprost be used with other glaucoma medications?
Yes, Bimatoprost can be combined with other glaucoma medications if prescribed by your doctor. Always follow your physician’s guidance on combining treatments.