Tamsulosin Hydrochloride is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist commonly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It relaxes the smooth muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, improving urinary flow and reducing symptoms of BPH. This guide explores the structure, properties, pharmacology, uses, and safety of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride.
1. Structure of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride
The molecular structure of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride explains its specificity for alpha-1 adrenergic receptors and its ability to reduce smooth muscle tension.
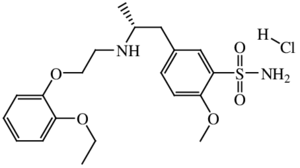
2D Structure
The 2D structure of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride features a sulfonamide moiety and an ether group attached to a benzene ring. These groups are crucial for its selective binding to alpha-1 adrenergic receptors.
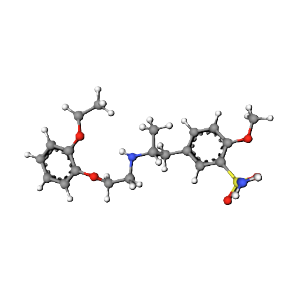
3D Structure
The 3D conformation of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride highlights its ability to fit into the active site of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the prostate and bladder neck, blocking norepinephrine-induced contractions.
2. Names and Identifiers
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride is recognized under various names and identifiers in medical and pharmacological databases.
- IUPAC Name:
5-[(2R)-2-[[2-(2-ethoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]propyl]-2-methoxybenzenesulfonamide hydrochloride - Molecular Formula:
C20H28N2O5S • HCl - Molecular Weight:
444.98 g/mol - CAS Registry Number:
106463-17-6 - Synonyms:
Flomax, Omnic
Explore a leading manufacturer of APIs.
With over 10 years of expertise, we ensure GMP compliance and provide reliable, high-quality solutions.
3. Chemical and Physical Properties
The chemical and physical properties of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride contribute to its specificity and pharmacological activity.
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Melting Point | ~230°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, methanol, and ethanol |
| LogP (Partition Coefficient) | ~1.8 |
| Chemical Class | Alpha-1 Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist |
4. Drug and Medication Information
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride is primarily used to manage urinary symptoms associated with BPH.
Formulations
- Oral Capsules:
- Available in strengths of 0.4 mg.
Mechanism of Action
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride works by:
- Blocking Alpha-1 Adrenergic Receptors: Relaxes the smooth muscles of the prostate and bladder neck.
- Improving Urine Flow: Reduces resistance to urinary outflow, easing symptoms of BPH.
Dosage and Administration
- Recommended Dose:
- 0.4 mg taken once daily, 30 minutes after the same meal each day.
Dosage may be increased to 0.8 mg daily if needed.
- 0.4 mg taken once daily, 30 minutes after the same meal each day.
5. Pharmacology and Biochemistry
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride’s pharmacology emphasizes its selective action on alpha-1 receptors in the urinary tract.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption:
Rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with bioavailability of ~90%. - Onset of Action:
Symptom relief observed within 1-2 weeks of continuous use. - Half-Life:
Approximately 9-13 hours. - Metabolism:
Extensively metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP3A4 and CYP2D6). - Excretion:
Eliminated primarily in urine as metabolites.
Pharmacodynamics
Tamsulosin selectively inhibits alpha-1A and alpha-1D adrenergic receptors in the prostate and bladder neck, reducing muscle tone and improving urinary flow without significantly affecting blood pressure.
6. Uses and Side Effects
Primary Uses
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
Alleviates urinary symptoms such as difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and frequent urination.
Benefits
- Effective symptom relief with once-daily dosing.
- Minimal impact on blood pressure compared to non-selective alpha-blockers.
- Improves quality of life for patients with BPH.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Fatigue.
- Nasal congestion.
- Abnormal ejaculation (e.g., reduced volume).
Rare but serious side effects:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, swelling).
- Priapism (prolonged, painful erection).
- Low blood pressure (hypotension).
Consult your doctor if side effects persist or worsen.
7. Safety and Hazards
Safety Profile
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride is safe for most patients when used as directed. However:
- Contraindications: Not suitable for patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity to Tamsulosin or its components.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Not indicated for use in women.
Chemical Safety

Handling Precautions
- Store at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight.
- Keep out of reach of children.
Environmental Impact
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride is biodegradable and poses minimal environmental risks when disposed of according to guidelines.
Chemignition Laboratory is a globally trusted manufacturer and exporter of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API).
We specialize in APIs and provide complete documentation support including,
- GMP Certificate
- COA
- MSDS
- Stability Data
- Impurity Profile
- ISO 9001 Certificate
Customized packaging and cold chain logistics ensure safe delivery of sensitive APIs worldwide.
We proudly serve pharmaceutical companies across the USA, Europe, Asia, and more.
Partner with Chemignition Laboratory for consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and reliable global supply.
FAQs
IUPAC Name of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride?
5-[(2R)-2-[[2-(2-ethoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]propyl]-2-methoxybenzenesulfonamide hydrochloride.
Molecular Formula of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride?
C20H28N2O5S • HCl
Molecular Weight of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride?
444.98 g/mol
CAS Number of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride?
106463-17-6
What is Tamsulosin Hydrochloride used for?
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride is primarily used to treat:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Relieves urinary symptoms such as difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and frequent urination caused by an enlarged prostate.
How does Tamsulosin Hydrochloride work?
Tamsulosin Hydrochloride works by blocking alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the prostate and bladder neck. This relaxation of smooth muscle reduces urinary obstruction and improves urine flow.
