Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) is a thiazide diuretic widely used to manage hypertension and edema associated with various medical conditions. Its mechanism of action, chemical properties, and safety profile make it a cornerstone in cardiovascular and renal medicine. This guide provides a detailed overview of Hydrochlorothiazide’s structure, properties, pharmacology, uses, and safety.
1. Structure of Hydrochlorothiazide
The molecular structure of Hydrochlorothiazide underpins its efficacy as a diuretic.
2D Structure
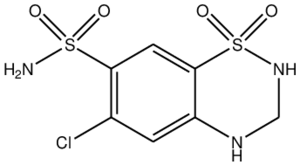
Hydrochlorothiazide’s 2D structure features a benzothiadiazine backbone with sulfonamide groups. These groups are critical for its diuretic action by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the kidneys.
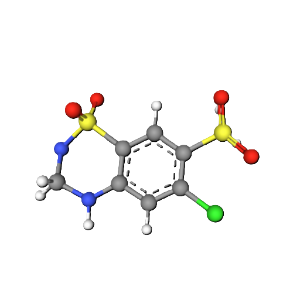
3D Structure
The 3D conformation of Hydrochlorothiazide highlights its spatial orientation, enhancing its binding to the sodium-chloride symporter in renal tubules. This precise interaction facilitates its ability to promote diuresis and reduce blood pressure.
2. Names and Identifiers
Hydrochlorothiazide is documented under various names and identifiers in medical literature.
- IUPAC Name:
6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1λ⁶,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide - Molecular Formula:
C7H8ClN3O4S2 - Molecular Weight:
297.73 g/mol - CAS Registry Number:
58-93-5 - Synonyms:
HCTZ, Hydrodiuril, Microzide
These identifiers facilitate the recognition of Hydrochlorothiazide in pharmacological databases.
3. Chemical and Physical Properties
The chemical and physical properties of Hydrochlorothiazide contribute to its therapeutic effectiveness.
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Melting Point | ~268°C |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol |
| LogP (Partition Coefficient) | ~0.07 |
| Chemical Class | Thiazide Diuretic |
These properties allow Hydrochlorothiazide to be formulated for oral administration.
Explore a leading manufacturer of APIs.
With over 10 years of expertise, we ensure GMP compliance and provide reliable, high-quality solutions.
4. Drug and Medication Information
Hydrochlorothiazide is widely used for managing cardiovascular and renal conditions.
Formulations
- Oral Tablets and Capsules:
- Available in strengths of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg.
- Combination Medications:
- Frequently combined with other antihypertensive drugs like lisinopril or losartan.
Mechanism of Action
Hydrochlorothiazide works by:
- Inhibiting Sodium Reabsorption: Blocks the sodium-chloride symporter in the distal convoluted tubules of the kidney.
- Promoting Diuresis: Increases sodium and water excretion, reducing blood volume and pressure.
- Lowering Peripheral Vascular Resistance: Contributes to its antihypertensive effect over time.
Dosage and Administration
- For Hypertension: 12.5-25 mg orally once daily.
- For Edema: 25-100 mg daily in one or two divided doses.
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for optimal results.
5. Pharmacology and Biochemistry
Hydrochlorothiazide’s pharmacology underlines its role in managing hypertension and fluid overload.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption:
Rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with bioavailability of ~70%. - Onset of Action:
Diuresis begins within 2 hours of administration. - Half-Life:
6-15 hours, depending on renal function. - Excretion:
Primarily excreted unchanged in urine.
Pharmacodynamics
Hydrochlorothiazide decreases sodium and fluid retention, which reduces blood volume. It also relaxes blood vessels, leading to a sustained antihypertensive effect.
6. Uses and Side Effects
Primary Uses
- Hypertension:
First-line treatment for high blood pressure, often in combination with other drugs. - Edema:
Manages fluid retention due to heart failure, liver disease, or kidney disorders. - Calcium Nephrolithiasis Prevention:
Reduces calcium excretion in urine to prevent kidney stones.
Benefits
- Effective in lowering blood pressure and preventing cardiovascular events.
- Reduces swelling and fluid overload.
- Minimal systemic effects at low doses.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Increased urination.
- Electrolyte imbalances (e.g., low potassium or sodium).
Rare but serious side effects:
- Severe dehydration.
- Allergic reactions like rash or swelling.
- Increased blood sugar or uric acid levels.
Consult your doctor if side effects persist or worsen.
7. Safety and Hazards
Safety Profile
Hydrochlorothiazide is generally safe when used as prescribed. However:
- Contraindications: Not suitable for patients with severe kidney disease, anuria (absence of urine), or hypersensitivity to sulfonamides.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Use with caution; consult your doctor before use.
Chemical Safety

Handling Precautions
- Store in a cool, dry place away from sunlight.
- Keep out of reach of children.
Environmental Impact
Hydrochlorothiazide is excreted in urine and may persist in aquatic systems. Proper disposal is recommended to minimize environmental impact.
Chemignition Laboratory is a globally trusted manufacturer and exporter of Hydrochlorothiazide Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API).
We specialize in APIs and provide complete documentation support including,
- GMP Certificate
- COA
- MSDS
- Stability Data
- Impurity Profile
- ISO 9001 Certificate
Customized packaging and cold chain logistics ensure safe delivery of sensitive APIs worldwide.
We proudly serve pharmaceutical companies across the USA, Europe, Asia, and more.
Partner with Chemignition Laboratory for consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and reliable global supply.
FAQs
IUPAC Name of Hydrochlorothiazide?
6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1λ⁶,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide.
Molecular Formula of Hydrochlorothiazide?
C7H8ClN3O4S2
Molecular Weight of Hydrochlorothiazide?
297.73 g/mol
CAS Number of Hydrochlorothiazide?
58-93-5
What is Hydrochlorothiazide used for?
Hydrochlorothiazide is used to treat:
- Hypertension: Lowers blood pressure to reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack.
- Edema: Manages fluid retention caused by heart failure, kidney disease, or liver disorders.
- Kidney Stones Prevention: Reduces calcium excretion in urine to prevent calcium-based kidney stones.
How does Hydrochlorothiazide work?
Hydrochlorothiazide works by inhibiting sodium and chloride reabsorption in the distal tubules of the kidneys. This action increases urine production, reduces fluid retention, and lowers blood pressure.
Can Hydrochlorothiazide be used long-term?
Yes, Hydrochlorothiazide is often prescribed for long-term use to manage chronic conditions like hypertension. Regular monitoring of kidney function and electrolytes is recommended.
